Best practices
This page covers some of the tasks that you may face while contributing. The approaches mentioned here are designed to make the process easier and may be applied to other projects hosted on GitHub or similar platforms.
Introduction
For more information on Git and GitHub, see GitHub Documentation
Git is a version control system which helps manage changes to files. The osu! wiki's data and history of changes are stored in a Git repository. GitHub is a platform for development that provides a web interface for Git repositories and offers a set of tools for project management.
Syncing the fork
In order to make changes to a repository located on GitHub, a potential contributor needs to obtain a controlled copy of it called a fork. When you create your fork of the osu-wiki repo, you take a snapshot of its contents at this very moment. To make a meaningful contribution, always sync your fork before making a set of changes — this can be done directly from GitHub:
Go to your fork of the
osu-wikirepo.Select the
masterbranch from the dropdown.Click
Fetch upstream, and selectFetch and merge.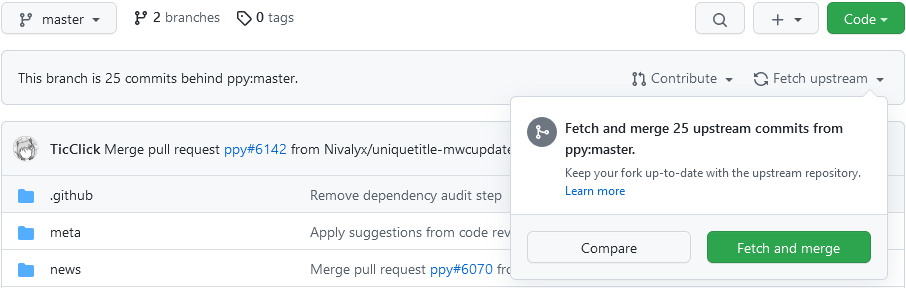 Updating the outdated branch
Updating the outdated branch
Now your branch is up-to-date with the original repository.
This solution works fine in most cases, although the feature itself has limited capabilities. For example, it doesn't allow you to overwrite any unwanted changes on the branch, as it only merges the upstream master branch.
If you encountered any problems while using the GitHub tool or you want to overwrite your branch's contents, you can use the workflow written by the osu! wiki contributors.
Open your fork and go to the
Actionstab.On the left sidebar, look for
Sync with ppy:master.Click
Run workflowand fill in the options: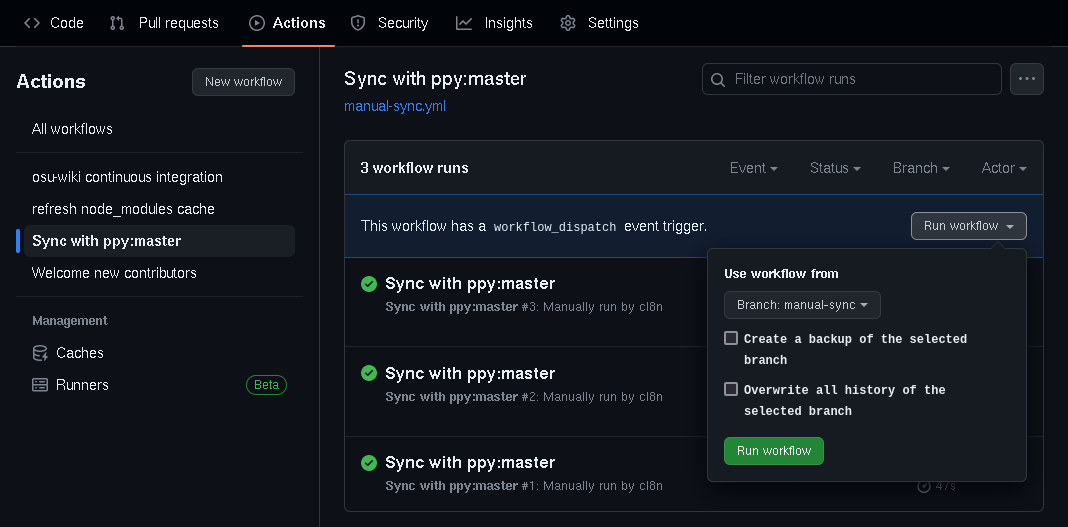 GitHub Actions workflow dispatch menu
GitHub Actions workflow dispatch menu- Use workflow from: Target branch that you want to sync. By default, it is set to
master. - Create a backup of the selected branch: Creates a copy of the target branch at
{branch name}-backupon your fork before attempting to update it. - Overwrite all history of the selected branch: Replaces the target branch with
ppy:master, discarding all of its differing commits. By default,ppy:masterwill be merged into the target branch.
Click the
Run workflowbutton and wait for the workflow to complete. If you're curious about how the tool works, click on theSync with ppy:masterworkflow task.
Making edits
See also: Forking Workflow | Atlassian Git Tutorial
Within your fork of the osu! wiki, you are free to make any changes and save them. Commits are individual "save points" of the repository. Branches are workspaces, which let you switch between multiple versions of the repository. To make your workflow easier and keep the history of the wiki clean and free from noise, follow these guidelines:
- Always start the work by creating a new branch off
master, and only keep your changes in there. Give it a meaningful name, such asupdate-staff-log. - Commit your work when you've made reasonably sized changes. It's better to commit an article as a whole rather than 10 small edits.
- Use short and meaningful commit messages, as they let others know what's in the box. Something like
Rewrite the section about jump patternssays a lot more thanUpdate en.md.
Opening a pull request
A pull request shows other people how your edits will affect the files. Add some information to your pull request to explain your intentions:
Title: a very short descriptive title for your changes in English, together with the article's name. In case of a translation, start with the two-letter language name of your translations in brackets. Examples:[FR] Add `BBCode`Update `Beatmapping` and `Beatmap/Difficulty`
Description: anything you want to signal to the maintainers and other potential reviewers. Examples:- A short summary of the changes, especially if they affect several articles
- The pull request's completeness, or ideas related to it
- Make sure to tick the
Allow edits from maintainerscheckbox, as it will allow the wiki maintainers to help you improve the pull request when necessary
Applying reviews
Reviews are best applied directly through the GitHub web interface. Use the Add suggestion to batch button when in the Files changed tab to apply multiple reviews simultaneously.
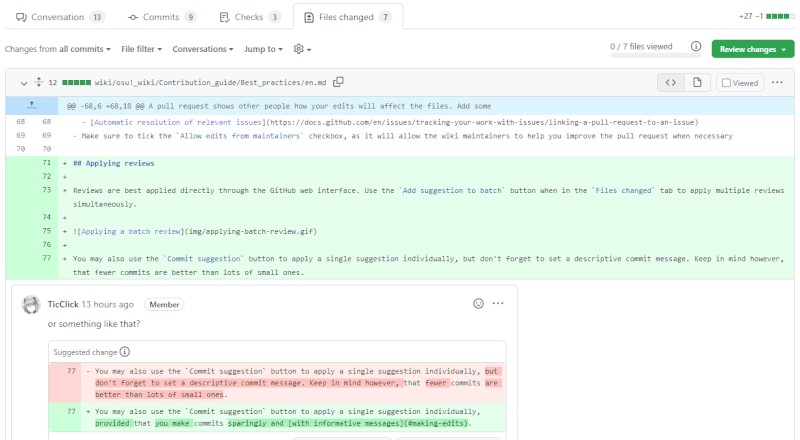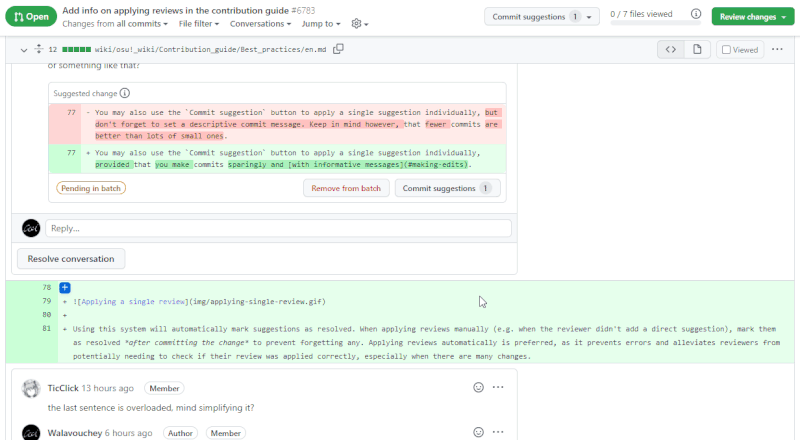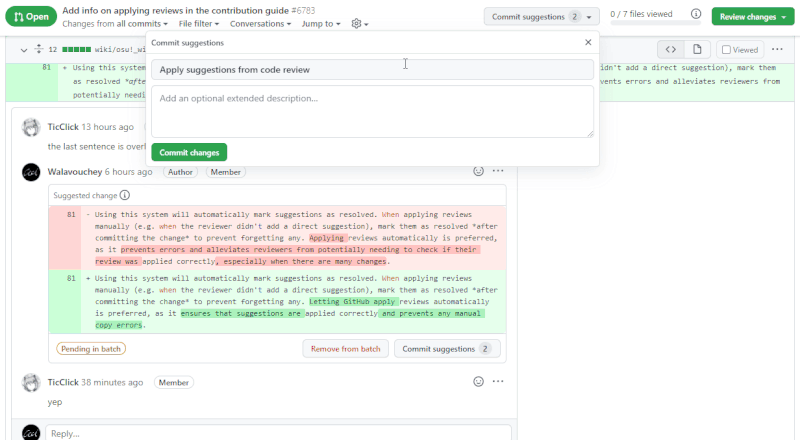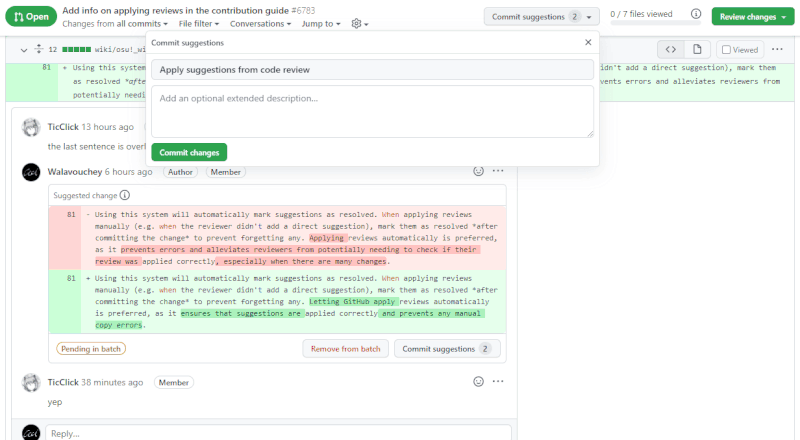
You may also use the Commit suggestion button to apply a single suggestion individually, provided that you make commits sparingly and with informative messages.
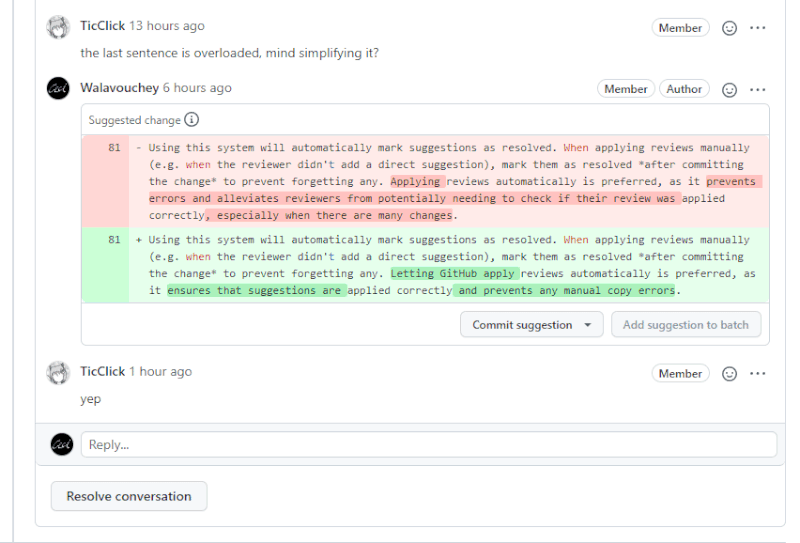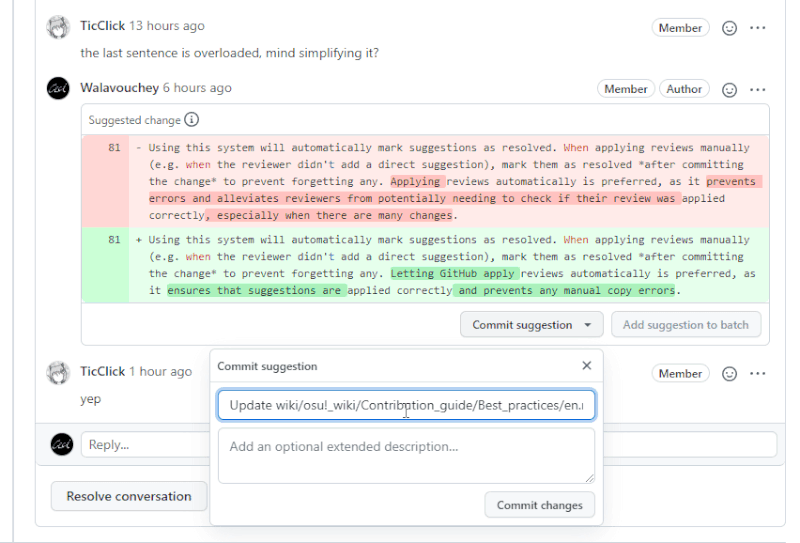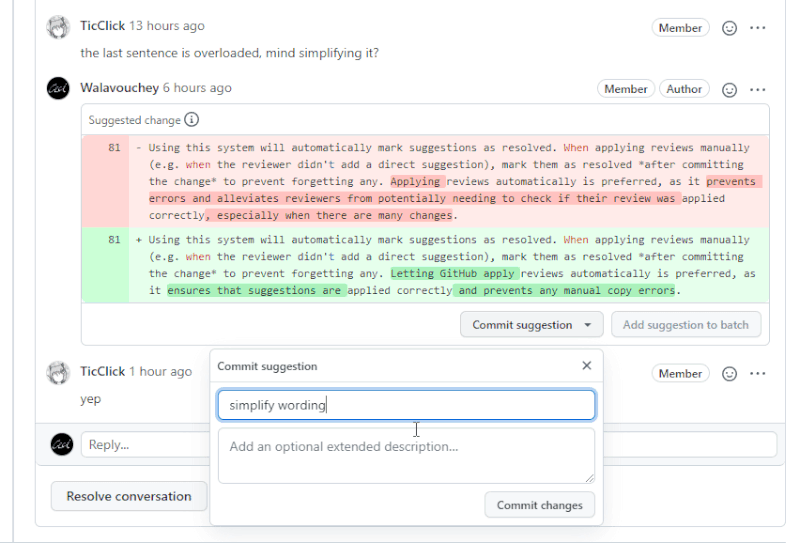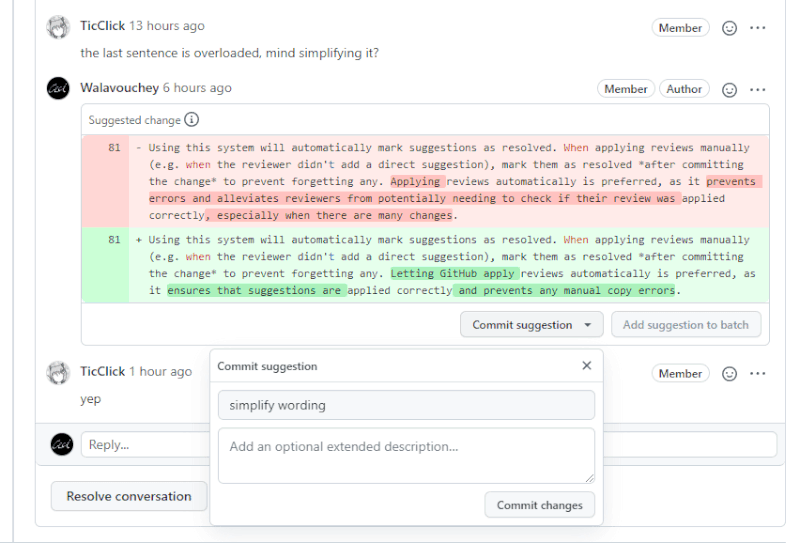
Using this system will automatically mark suggestions as resolved. When applying reviews manually (e.g. when the reviewer didn't add a direct suggestion), mark them as resolved after committing the change to prevent forgetting any. Letting GitHub apply reviews automatically is preferred, as it ensures that suggestions are applied correctly and prevents any manual copy errors.
Resolving conflicts
There are two reasons for why a conflict could have happened:
- You edited a file when your branch was out of date.
- There was a lack of communication between you and another person, so you both were editing the same article. The other person's changes were merged before yours, which caused your edited files to become out of date.
Depending on the severity of the conflicts, you have two options on how to fix this:
- If your pull request has the
Resolve conflictsbutton, click on that. This will open a slightly different version of the web editor.- GitHub will highlight the conflicting areas. Find one of them.
- Everything from
<<<<<<<to the=======is your changes, whereas everything from=======to>>>>>>> masteris what's in theppy/masterbranch. - From here, you will need to manually fix the conflict and delete the lines with the
<<<<<<<,=======, and>>>>>>> mastermarkings. - Repeat the process for all conflicts.
- When completed, click
Mark as resolved(this is only available when all conflicting parts of the file are resolved).
- If the
Resolve conflictsbutton is blocked due to the conflicts being too complicated for GitHub, you are out of luck and will need to update your branch and make your changes again.- Note: This is only true if you are limited to using the GitHub web interface. There are still ways to fix it, but they don't belong to the scope of this article. Moreover, it is probably not worth the effort to do so, because you will overwrite and revert the conflicting changes.
 Updating the outdated branch
Updating the outdated branch GitHub Actions workflow dispatch menu
GitHub Actions workflow dispatch menu